Chimpanzee
Chimpanzee Facts
| Size | 25-37 inches (64-94 cm) (body length) |
| Speed | Up to 25 mph (40 km/h) |
| Weight | 55-154 pounds (25-70 kg) |
| Lifespan | 30-40 years |
| Food | Leaves, fruits, nuts, insects, small mammals |
| Predators | Leopards, crocodiles, snakes |
| Habitat | Africa |
| Order | Primates |
| Family | Hominids |
| Scientific name | Pan |
| Characteristics | Human-like primate |
Main Characteristics
Chimpanzees are intelligent primates that are capable of recognizing themselves in a mirror and using tools. They belong to the hominid family because they are closely related to us humans.
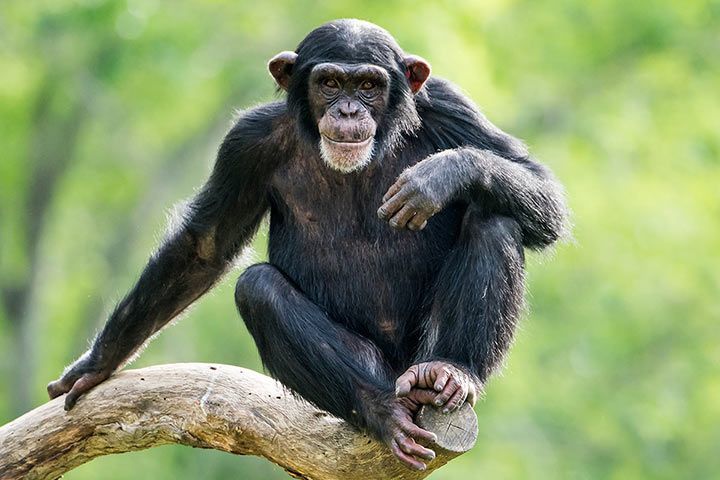

Species
The chimpanzee family includes the “common” (= normal) chimpanzee and the bonobo. They evolved independently about 1.5 to 2 million years ago, when the Congo River emerged and separated them spatially.
Closest Human Relatives
Chimpanzees and bonobos are 98% human, which means that their genetic makeup is 98% identical to ours. This means that we are genetically most closely related to them. And yet we are very different in appearance, physique and intelligence. It's stunning that 2% can make such a difference.
Distribution and Habitat
Chimpanzees live in Africa. They are common in the following countries: Senegal, Mali, Guinea, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Ivory Coast, Ghana, Nigeria, Cameroon, Gabon, Equatorial Guinea, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Central African Republic, Uganda and Tanzania. They prefer to inhabit moist, dense rainforests, but can also thrive in dry, treeless savannahs.
Life Style
Chimpanzees are diurnal. They spend most of their time in trees, swinging from branch to branch in search of food. They are very social and live in families of six to ten members. When several families come together, they form communities of up to 100 animals. They spend their nights up in the trees, creating a cozy nest to rest in.
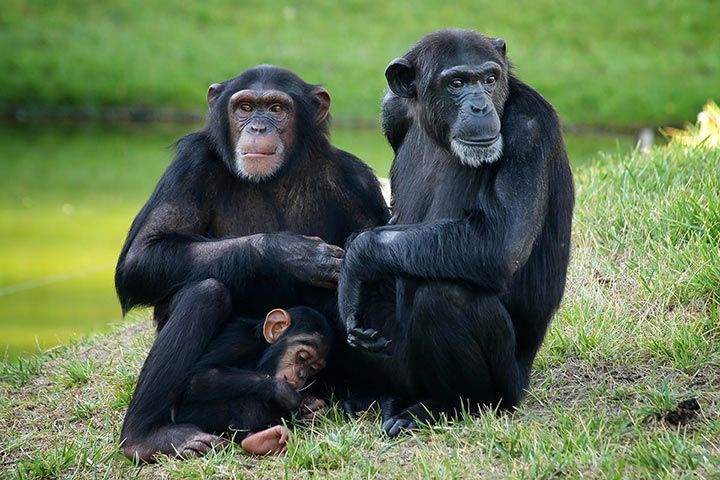

Anatomy and Appearance
Size and Weight
Chimpanzees have strong, robust bodies. Their body length is 25-37 inches (64-94 cm). When they stand upright, they grow to 40-66 inches (100-170 cm) tall. The males are significantly heavier. They weigh 77-154 pounds (35-70 kg). The females weigh 55-110 pounds (25-50 kg).
Fur
Chimpanzees sport a coat of dark brown to black fur, with the exception of their face, fingers, palms, toes, and soles of the feet, which are completely hairless. Older chimpanzees often have the same problems as their human relatives: They lose their hair! When they get older, their foreheads become bald and their beards slowly turn gray.
Head and Face
Chimpanzees have a round head, rounded ears, pronounced brow ridges and a prominent snout. They have sharp canine teeth that are significantly longer in males than in females. As they age, their faces become increasingly darker and they develop freckles.
Arms
Chimpanzees have very long arms. They become significantly longer than their legs. When their arms hang down, the hands reach below the knees.
Hands
Chimpanzees have opposable thumbs. For example, they can place their thumb opposite their index finger and grasp things like they would with a tweezer. This grip is also called a "pinch grip". Other animals with opposable thumbs include giant pandas, red pandas, koalas, opossums, other primates and chameleons. We humans also have such a thumb.
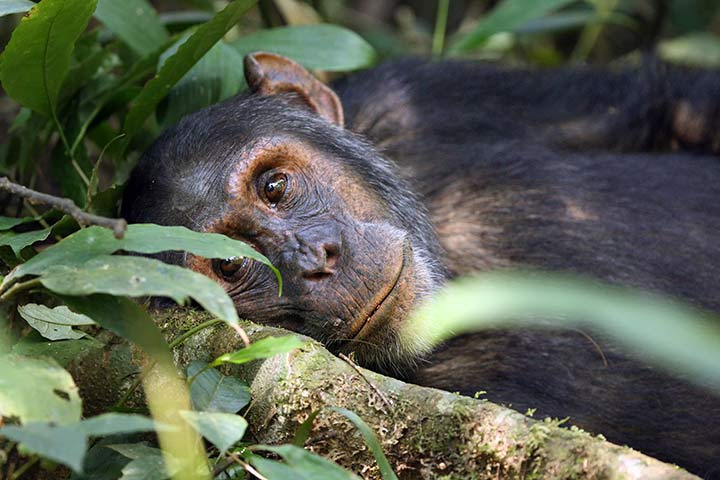

Diet
Chimpanzees are omnivores. However, their primary source of food is plants. They also feed on fruits and nuts, and occasionally eat insects and small mammals.
Behavior
Communication
Chimpanzees mainly rely on body language to communicate with other members of their species. They express themselves through actions like clapping their hands or grooming each other. They also communicate how they are feeling with their facial expressions. When they are frightened or excited, they distinctly show their teeth – humans often misinterpret this as a smile.
Locomotion
• Swinging
Chimpanzees spend most of their time in trees. They hold on with their arms and swing from branch to branch.
• Knuckle-Walking
When chimpanzees move on the ground, they usually do so on all fours. They place their hind feet on the soles of their feet as normal. However, they clench their hands into a kind of fist. Only the middle phalanges of the fingers touch the ground. The so-called knuckle-walk safeguards the delicate fingers required by animals to handle tools or grasp branches.
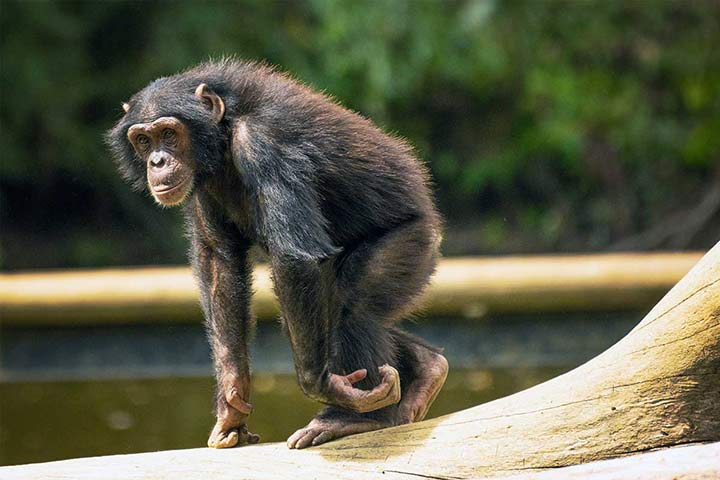
• Standing Upright
Chimpanzees occasionally stand on their hind legs, reaching a height of 40-66 inches (100 to 170 cm).

Aggressiveness
Are Chimpanzees Dangerous?
Chimpanzees are very strong and intelligent. However, they're wild animals that can't be domesticated. At times, their behavior is unpredictable and they can become aggressive. This makes them particularly dangerous for people who have no experience with the animals.
Do Chimpanzees Attack Humans?
• In the Wild
Generally, chimpanzees try to avoid humans. However, if they are cornered or feel threatened, they won't hesitate to attack. It's like this: We are taking away their habitat by building villages, roads and farms. Consequently, the primates are left with no option but to interact with us. Typically, they're individual animals desperately searching for food. Over the past two decades, Uganda has recorded a total of 20 incidents where humans have tragically lost their lives due to encounters with chimpanzees.
• As Pets
There are people who keep chimpanzees as pets - even though it is forbidden. That is very dangerous. In 2009, a chimpanzee attacked and seriously injured a woman in the United States. His name was Travis and he was kept as a pet. He even appeared in TV commercials. Travis attacked the woman, who was a neighbor of the owner, and wounded her so badly that she lost nine fingers, her eyes and her nose.
Do Chimpanzees Attack their Own Kind?
Chimpanzees sometimes engage in aggressive behavior, including attacking and even killing their fellow species. This can happen when they feel the need to protect their own territory or try to claim someone else's.
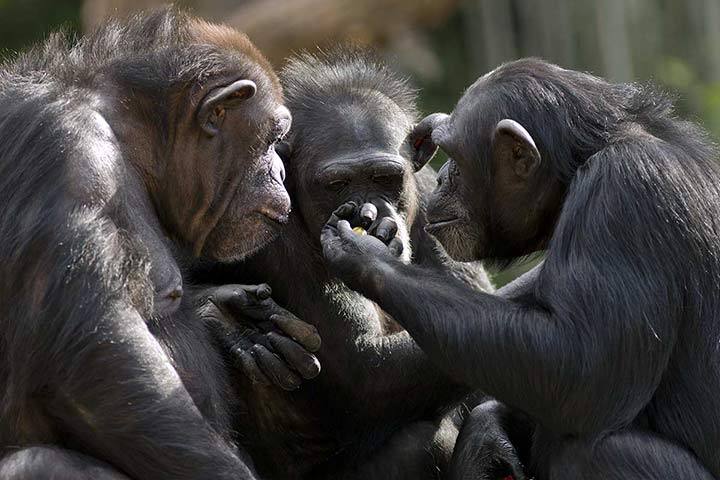

Strength
Are Chimpanzees Stronger than Humans? Yes, they're 1.5 times stronger than humans. They have twice as many white fast-twitch muscle fibers, which enable particularly fast, powerful movements. The gripping strength of a chimpanzee is 440-727 pounds (200-330 kg). A human has a grip strength of around 66-110 pounds (30-50 kg).
Chimpanzee vs. Human – Who Would Win?
Since chimpanzees are so similar to us, the question arises as to who would win a fight. The clear answer is: the chimpanzee. While humans may be bigger and more intelligent, the primates are known for their aggression, speed, strength, and ability to deliver a hard bite.
Chimpanzee vs. Gorilla – Who Would Win?
Gorillas are much bigger and heavier than chimpanzees. However, they are also less agile and not as nimble. On the flip side, they have a better ability to endure blows. In a fight, the gorilla would win because of its immense size and weight, making it impossible for the chimpanzee to combat. There have been stories of chimpanzees taking on gorillas in the wild, but they only succeeded when they teamed up as a group.

Intelligence
Medicine
Chimpanzees consume specific plants when they don't feel well or have injuries. The leaves are like medicine because they contain substances that, for example, cleanse their intestines of parasites. When they injure themselves, they crush insects and use them as a healing balm.
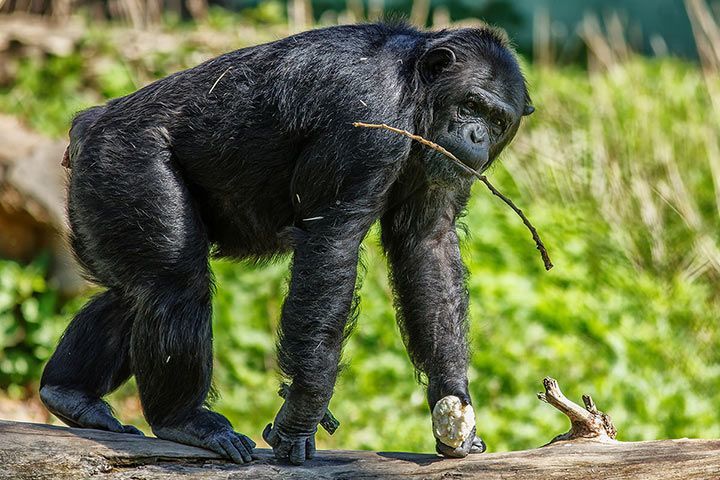
Tool Use
Chimpanzees use tools. They crack nuts by hitting them with stones or use thin sticks to get delicious termites out of their burrows. However, they're not the only ones using tools. Orangutans, ravens, elephants and otters also do this.
Humor
In 2020, researchers showed for the first time that chimpanzees have a sense of humor - just like us humans. They observed the animals offering objects to each other and unexpectedly withdrawing them at the last second. This kind of joke requires a high level of intelligence.
IQ
It is said that chimpanzees are smarter than a four-year-old child and that their intelligence quotient is 35 to 50. For comparison: Most people have an IQ between 85 and 115. However, testing the IQ of animals is difficult. And equating it with human IQ is questionable.
Importance for the Ecosystem
Chimpanzees play a crucial role in maintaining the balance in nature. By consuming plants and dispersing their seeds through their droppings, they significantly contribute to the biodiversity of their environment. Their actions foster the growth of a diverse range of plant species, ensuring a thriving ecosystem.
Life Expectancy
In the wild, chimpanzees live to be 30-40 years old. The oldest male chimpanzee, named Gregorie, lived to be 66 years old and the oldest female chimpanzee, named Little Mama, lived to be 70 years old.
Enemies and Threats
Natural Enemies
The natural enemies of chimpanzees are leopards, crocodiles and snakes.
Human Impact
According to the IUCN, chimpanzees are an endangered species and therefore under special protection. One of the biggest threats is the loss of their habitat due to deforestation and road construction. Farmers kill them because they eat their plants. They're also killed by poachers who sell their meat (so-called “bushmeat”). Another problem is illegal keeping as pets.
Conservation Status and Population
According to WWF and IUCN, there are 330,000-458,000 chimpanzees left. This is the total number of all four subspecies, based on estimates from 2011-2018 (as of November 2023). Currently, they're not threatened with extinction.
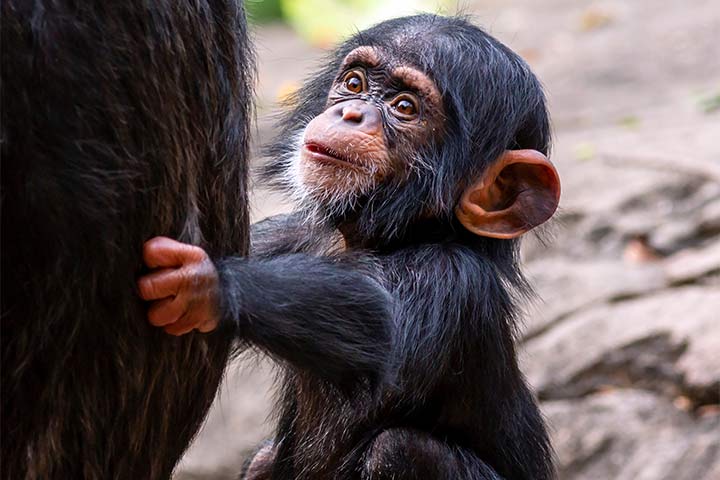

Reproduction
Chimpanzees become mature at an age of 13-16 years. After a gestation period of seven to eight months, they give birth to a young chimp. Baby chimpanzees first cling to their mother's belly. Later they ride on her back. They are breast-fed for three years. At the age of four they can walk. They stay with their mother until they're seven years old. At around 15 years old they're fully grown.
Evolution und Discovery
The way of life of chimpanzees was best known by Jane Goodall. The British researcher traveled to Tanzania in 1960 to study chimpanzees there. She is committed to protecting and preserving animals in an extraordinary way.
Fun Facts
What Does the Name Come From?
The word chimpanzee has its origins in the African Bantu languages. It derives from "ci-mpenz" or "chimpenze".
The Chimpanzee Is Related To:
Animals in the Same Biome:
Related Articles: