Beaver
Beaver Facts
| Size | 30-40 in (74-102 cm) body, 8-14 in (20-35 cm) tail |
| Speed | 5 mph (8 km/h) (while swimming) |
| Weight | 24-70 lb (11-32 kg) |
| Lifespan | 10-12 years |
| Food | Tree bark, water and riparian plants |
| Predators | Wolves, bears, lynxes |
| Habitat | Europe, North America |
| Order | Rodents |
| Family | Beavers |
| Scientific name | Castoridae |
| Characteristics | Second-largest rodent, scaly tail, webbed hind-feet |
Main Characteristics
The beaver is the world`s second largest rodent after the capybara. There is the European and the Canadian beaver. Beavers inhabit the banks of standing and flowing waters, where they build a lodge (for living and sleeeping) and dams (for thawing water).
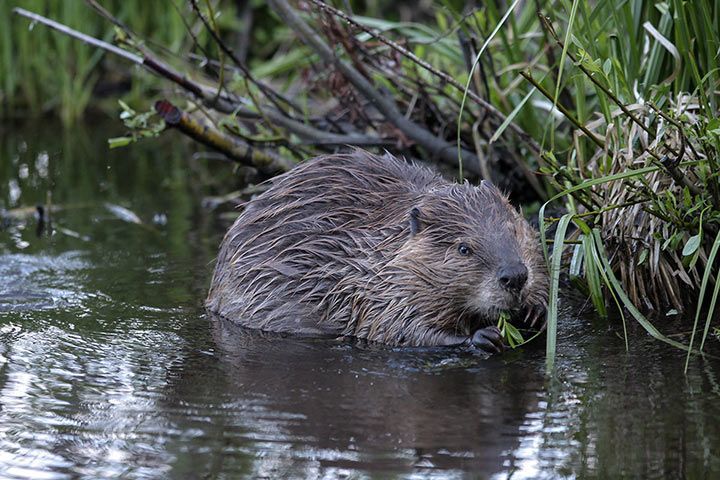

Anatomy and Appearance
Teeth
Why are beaver teeth yellow or even orange? Beavers do not brush their teeth. Ok, ok, that was a joke! Beavers have yellow or even orange teeth because their food, which is the trees and their bark, contains a lot of iron. This causes the enamel to be orange and super hard - which is very important for the beaver.
Fur
The beaver has an incredibly thick coat. Up to 23,000 fine hairs grow on one square centimeter of its skin, compared to the 600 on our skin. The coat protects the beaver from cold water. Some vain people also wear beaver-fur hats to protect their ears. The fur is one of the reasons why beavers have almost been exterminated. It is still an incredibly rare experience to come across a beaver, but fortunately the number of those animals is increasing again.
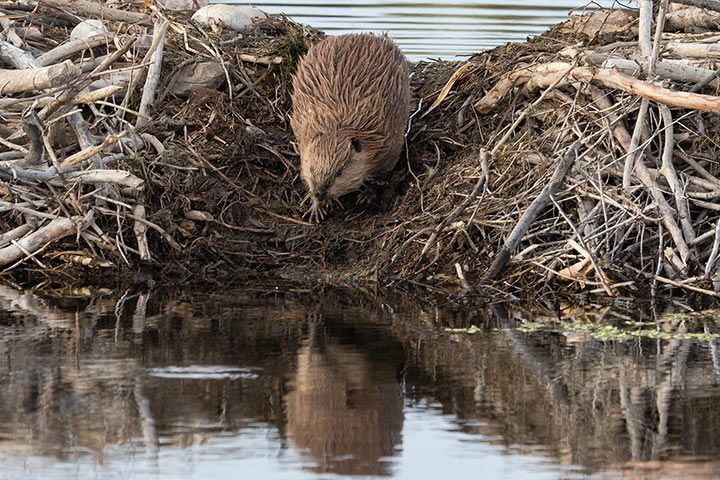

Diet
Beavers feed on tree bark as well as on water and riparian plants.
Lifestyle
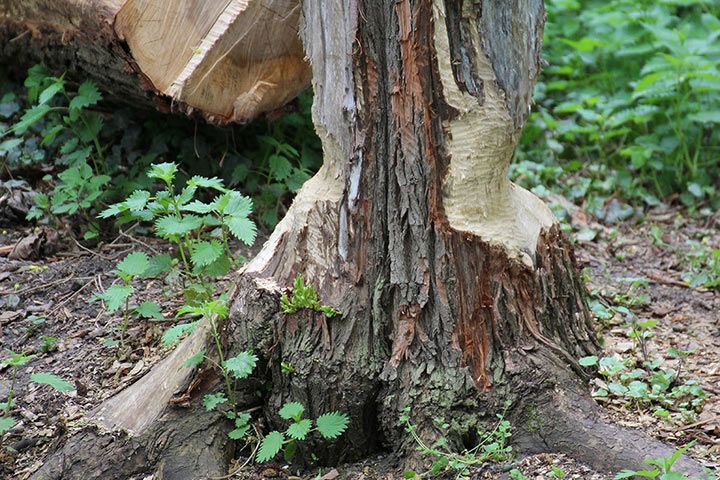
They Are Lumberjacks
Beavers are gifted architects. For their dams and lodges they cut down tree trunks up to 3.2 feet (1 meter) thick. They use their front teeth and their lower jaw to gnaw them off at the lower end. In the end, the shape of the tree resembles an hourglass and in the middle it is as thin as a tooth pick when it falls down noisily.
They Are Construction Workers
Afterwards the cut down tree is expertly cut up into handy little logs and transported to the beaver’s lodge. The beaver uses the material to repair its “home” and to dam up the water.
They Are Architects
Beaver constructions can be up to 5 feet (1.50 meters) high and 328 feet (100 meters) long. Yet, the beaver does not only build dams. If it feels comfortable with the current water level, it does not construct any dam. Why bother? At precipitous shorelines the beaver sometimes does not construct any dams at all but digs tunnels into the bank walls.
Beaver Dam and Beaver Lodge
Why Do They Build Dams?
The beaver lodge is the rodent’s living room, the fridge and a cosy place to sleep. Lynxes, wolves, bears or poaching dogs are not welcome there of course. Therefore the entrance is always UNDER water. In order to keep the water line at the same level all the time, the beaver constructs a dam.
The Largest Dam
In 2007 an extraordinarily large beaver dam was discovered in the Wood Buffalo National Park in Alberta (Canada). It is 2,788 feet (850 meters) long. Probably several generations of beavers have been working on it since 1970.
The Beaver Lodge
A beaver's lodge has several pipes for different puposes. There are food tunnels, escape tunnels, and tunnels for playing.

Enemies and Threats
The beaver's natural enemies include wolves, bears, lynxes, pumas and wild dogs.
Are They Endangered?
According to the IUCN (International Union for Conservation) beavers are no endangered species. Nevertheless, the European beaver is a particularly protected species in Germany and must not be hunted.
Unloved Species
Humans do not necessarily love beavers as they modify the shorelines so that adjacent areas become wetlands which then cannot be used as planned. Roads could also be washed out and damaged. On the other hand, the beaver is extremely important to maintain a healthy eco system.
Importance For the Ecosystem
Why are beaver dams important? With their dams the beavers create an important habitat for water plants, fish, insects and birds. They also stabilize the shoreline and prevent sand from filling the river. The dammed-up waters raise the groundwater level and alleviate the flood risk.
Reproduction
Beavers stay with their partners for their entire lives. Commonly they mate between January and April – under water. Usually they give birth to two or three babies after about 100 days. The young beavers stay with their parents for up to two years and then go their own ways.
Fun Facts
The Beaver Is Actually a Fish, Isn’t It?
In the Middle Ages, beavers often were categorized as fish because of their webbed feet, scaly tails and their habitat, as people were not allowed to eat meat during fasting periods.
The Beaver Is Related To:
- Gopher
- Kangaroo Mice
- Kangaroo Rats
Animals in the Same Biome:
- Alligator
- Bald Eagle
- Barn Owl
- Black Bear
- Brown Bear
- Great Spotted Woodpecker
- Kingfisher
- Peregrine Falcon
- Lynx
- Raccoon
- Tiger
- Wolf
Video: 31 Facts About Beavers
(Video opens on YouTube)