Eurasian Jay
Eurasian Jay Facts
| Size | 12-14 in (32-35 cm); 21-23 in (53-58 cm) (wingspan) |
| Speed | unknown |
| Weight | 5.6-6 oz. (160-170 g) |
| Lifespan | 16-17 years |
| Food | Acorns, insects, fruit, eggs, small vertebrates |
| Predators | Eagle-owl, marten, cat |
| Habitat | Europe, North Africa, Asia |
| Order | Passerines |
| Family | Corvids |
| Scientific name | Garrulus glandarius |
| Characteristics | Strong beak, very intelligent |
Main Characteristics
Eurasian jays are corvids, just like magpies and ravens. They live in dense deciduous and mixed woodland - but prefer oak woodland. In this animal factsheet, you’ll find out all about the life and behavior of the Eurasian jay.
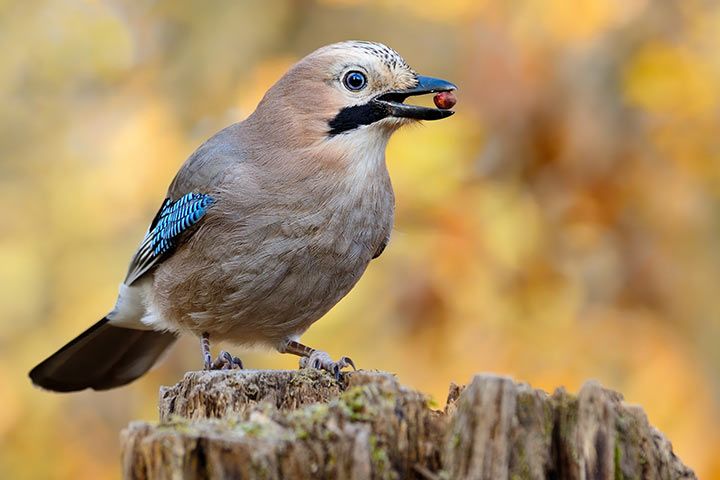

Anatomy and Appearance
Plumage
The Eurasian jay can be identified thanks to their characteristic plumage. It is light pink to red-brown with striking, shimmering blue-black banded feathers on its black and white wings. It has a long, narrow, black stripe on its cheek, extending the beak.
Throat Sack
The jay can carry 5 to 10 acorns at once in its throat sack, usually carrying one extra acorn in its beak as well. When you next go on a fall walk, collect 10 acorns and put them in one hand - that’s a lot for one bird to carry. Each year, one jay collects 24 to 33 pounds (11-15 kg) of acorns. They remember 25,000 to 30,000 hiding places over the course of their lives.
Diet
What do Eurasian jays eat? Acorns, mostly - but not just acorns! In summer, jays eat bugs, beetles, grasshoppers, spiders, fruit, eggs and small vertebrates. They even indulge in a little carrion. In winter, jays mostly eat acorns, beechnuts and other nuts. They gather these in fall and hide them in the ground to see them through winter.
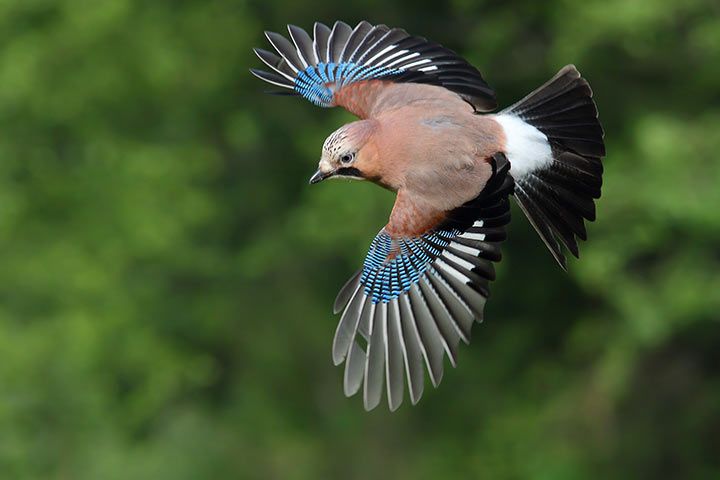

Behavior
Anting
What would you do if you had annoying parasites on your skin? Well, if you were a Eurasian jay? This bird has a pretty clever trick. Every few days, it sits right on top of an anthill and spreads its wings. It then starts to hit and rub at the ground. The ants don’t like this one bit. To get rid of this intruder, the ants spray acid right into the jay’s feathers. And this expels the parasites. Starlings also do this. The technical term for this is “anting”.

Senses and Abilities
Mimic Sounds
Eurasian jays often sound like rattling ratchets. But they’re not always identifiable by their call. They “copy” sounds from their environment. If they feel threatened, they will mimic a predator - a tawny owl, a buzzard or hawk - to scare their enemies off. Scientists believe that jays link sounds with the situation where they first heard them. A relaxed jay might mimic a woodpecker, sparrow or even the casual whistling of a human. And now the interesting bit. Jays that live in or nearby cities begin mimicking very different sounds. They might sound like screeching tires, a crying baby, a lawnmower, a meowing cat or an alarm clock. We also have a detailed article about birdsong.
Intelligence
Jays are very intelligent. The Males think about what their lady friends might want to eat. This was found out using an experiment. Male jays were allowed to watch their partners being fed waxworms. They were then able to bring them something themselves, choosing between waxworms and mealworms. Without exception, they all brought their lady friends the food that they hadn’t tried yet: mealworms. And it was the same the other way round: if the partners had eaten mealworms, the males brought them the waxworms instead. How romantic, and clever!
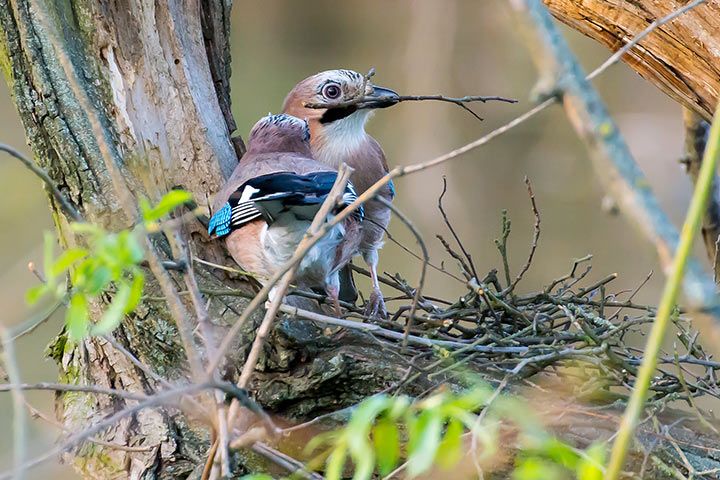

Importance for the Ecosystem
Jays are known as acorn-planting machines, as they hide so many acorns and don’t manage to find all of them again. This helps to reforest woodland, contributing to keeping nature in balance. They also make sure that bacteria and disease don’t spread by eating carrion.
Reproduction
Jays are monogamous, which means they stay with one partner their whole lives. During mating season, they reinforce their partnerships through flapping their wings in a specific way as well as zigzag or circular flight. One clutch usually contains 4-7 eggs. These are gray-green in color with brown speckles. After 16-19 days, the chicks hatch. They then spend 19-23 days in the nest. Once they leave the nest, they’re still fed for another 3-4 weeks.